Background: The persistence or recurrence of minimal residual disease (MRD) after chemotherapy predicts relapse of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor-modified T (CD19 CAR-T) cells have shown excitable response in B-ALL. Recently, some studies have shown that ALL patients with lower burden had higher CR rate and lower risk of CRS after CAR-T therapy (Park, et al, NEJM. 2018; 378(5):439-448. Lee, et al, Blood.128 (22):Abstract 218.). However, its role in chemotherapy-refractory MRD-positive B-ALL remains unclear. Here we aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of CD19 CAR-T in MRD-positive B-ALL patients.
Methods: Since January 2018, a total of 14 B-ALL patients with persistent (n=8) or recurrent (n=6) MRD were enrolled in the CAR-T clinical trials (ChiCTR-ONN- 16009862 and ChiCTR1800015164). The patients were from two different clinical trials about CAR-T. If patients were treated in an MRD positive state, they would be included in this analysis. All the patients received one or more infusions of autogenous CD19 CAR-T.
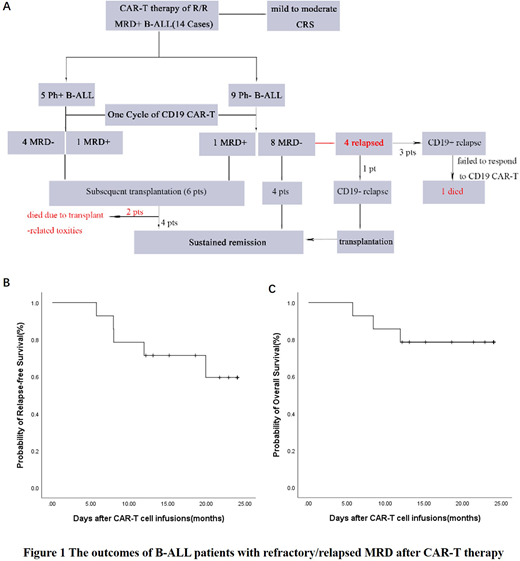
Results: Median age was 37.5 (13-62) years and 7 patients were female. The median dose of infused CAR-T cells was 6.78´106cells/kg, and 5 patients received more than one infusion. After one cycle of CAR-T infusion, 12 patients achieved MRD-negative remission, leading a response rate of 85.7%. Of the subgroup of 5 Ph-positive patients who subsequently underwent transplantation, 2 patients died due to transplant-related toxic effects, whereas the other 3 patients all currently alive without leukemia. Of the subgroup of 9 Ph-negative patients, 8 patients did not undergo subsequent transplantation (Figure 1). Three patients finally suffered CD19-positive relapse and 1 patient suffered CD19-negative relapse. Importantly, 4 patients (50%) are in ongoing molecular remission without transplantation, with a duration of response averaging 22.9 months (range: 12.1-28.6 months).
The most frequent adverse events were fever and hematopoietic toxicities. Ten patients (71.4%) had grade 1 or 2 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and no patients died of CRS. At a median follow-up time of 599.5 days (range: 172-915 days), the probability of 2-year relapse-free survival and 2-year overall survival was 61.2%±14.0% and 78.6%±11.0%, respectively.
Conclusion: In conclusion, pre-emptive CD19 CAR-T treatment is an effective and safe approach and may confer a sustained remission in B-ALL patients with chemotherapy-refractory MRD.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal